- HOME
- Sustainability
- CSR Activity Report (CSR Guideline Activity Reports)
- Safety, Accident Prevention, and Environmental Preservation
- Managing Energy Use and Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Managing Energy Use and Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Seeking to contribute to a carbon-neutral world, Toray Group pursues initiatives for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
In the Toray Group Sustainability Vision announced in July 2018, the Group set out the target of reducing greenhouse gas emissions1 from production activities per unit of revenue by 30% compared with the baseline year of fiscal 2013 across the entire Toray Group worldwide as a quantitative target for fiscal 2030. In its CSR Roadmap 2022, the Group set out an interim target of reducing greenhouse gas emissions per unit of revenue1 Group-wide by 20% by fiscal 2022 compared with fiscal 2013. As a result of efforts to reduce CO2 emissions during manufacturing by conserving energy with improved manufacturing processes, increasing utilization of renewable energy, and reducing coal consumption, the Group reduced greenhouse gas emissions per unit of revenue by 34.6%2 by the end of fiscal 2022.
In March 2023, the target set out in the Toray Group Sustainability Vision for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from production activities per unit of revenue was raised significantly from a 30% reduction compared with the baseline year of fiscal 2013 to a reduction of more than 50%1. The Group also set a target of reducing absolute greenhouse gas emissions for Toray Group in Japan by at least 40%1 compared to fiscal 2013, thereby accelerating the Toray response to climate change.
As of the end of fiscal 2024, the Group as a whole achieved a 42.8% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions per unit of revenue, and a 28% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions within Japan.
- 1 Scope 1 (direct emissions from plants, offices, and vehicles, etc. owned by the Group) and Scope 2 (indirect emissions resulting from the production of electricity and other energy consumed by the Group) emissions.
- 2 Until fiscal 2022, this was calculated by multiplying the GHG emissions and revenue of individual subsidiaries worldwide by the applicable Toray Industries' equity share. In fiscal 2023 however, the calculation method changed, and the degree of financial control Toray Industries has over the individual subsidiary (not the equity share) is now used, in accordance with the GHG Protocol, the international standard. For fiscal 2022, the reduction calculated under this new method would be 32.7%.
Managing Energy Use
As part of its energy management, Toray Group sets annual energy-conserving targets for each company and plant and promotes group-wide energy-conserving activities. It also checks the progress of its energy-conserving measures on a monthly basis.
Toray Industries undergoes audits of its environmental data, including energy consumption, to identify opportunities for improving its energy performance. Using the results as a reference, the Company is promoting energy-conserving activities with a goal of reducing its per-unit energy consumption3 by 2% annually.
In fiscal 2024, energy consumption decreased by 0.9% year on year due to more efficient use of energy and efforts to reduce energy waste and loss. Meanwhile, energy intensity improved by 3.2% year on year, reflecting a 1.4% increase in production volumes. This represents an 11.2% improvement over the baseline year of fiscal 1990.
- 3 Energy consumption per converted production volume
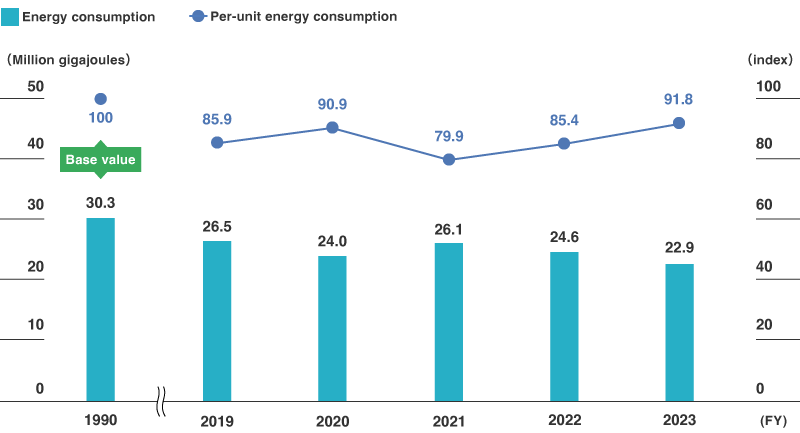
Note: The energy consumption shown in this graph does not include renewable energy.
Toray Group holds an annual group-wide energy-saving technology presentation meeting each June as part of its energy conservation activities, where the Group shares and recognizes the results of its energy-saving initiatives. This initiative is aimed at raising employees’ awareness of energy conservation and promoting the deployment of effective technologies across group companies.
At the meeting, about 20 energy-saving projects nominated by Toray Group companies are reviewed, and four to five outstanding cases are selected for recognition. Presenters explain the background and key points behind their projects, the technical innovations applied, and the challenges they faced in implementation. Approximately 300 employees, including both in-person attendees and online participants, usually take part in the event.
In fiscal 2024, the following plants and group companies took part:
- Toray Industries, Inc.: Nagoya Plant, Tokai Plant
- Group companies in Japan: Du Pont-Toray Co., Ltd., Toray Fine Chemicals Co., Ltd.
- Group companies outside Japan: Toray Fibers (Nantong) Co., Ltd.
Furthermore, as part of its concrete on-site support, Toray Group has organized teams whose members are well-versed in manufacturing processes and equipment. These teams conduct energy-saving diagnostics at Toray Industries and group company plants around the world to generate ideas for further energy conservation and actively promote activities to achieve this. In fiscal 2024, these diagnostics were carried out at three of Toray Industries’ plants. As a result, the Group reduced greenhouse gas emissions by about 5,000 tons-CO2 per year or more equivalent.
Finally, in conjunction with these diagnostics, Toray Group also implements an energy conservation education program aimed at raising employee awareness of energy efficiency. To date, 463 employees have participated in this program.
Toray Group Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 1 and 2)
Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions per unit of revenue (%)
- ■Reporting scope
- Toray Group
- ■Target
- At least 40% lower than fiscal 2013 (Fiscal 2025)
Result in fiscal 2024
42.8%
Toray Group's greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 and 2) reduction target was established in the CSR Roadmap 2025. The Group as a whole implements systematic reduction measures with the goal of achieving a 40% reduction of greenhouse gas emissions per unit of revenue by fiscal 2025, compared to fiscal 2013.
Overall greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 and 2) for Toray Group in fiscal 2024 decreased by 6.3% year on year to 4.64 million tons-CO2 equivalent. In terms of per unit of revenue, the Group reduced emissions by 42.8% compared to the baseline year of fiscal 2013. In addition to an increase in groupwide sales revenue, the reduction was due to efforts to achieve a maximum reduction of greenhouse gas emissions (such as improving processes to conserve energy, utilizing renewable energy, and reducing coal use at group plants).
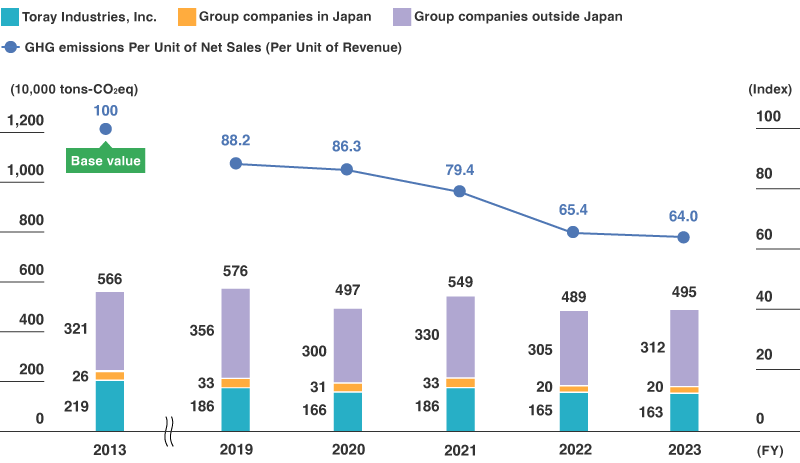
Notes:
- Figures for the baseline year of fiscal 2013 are calculated using Japanese GAAP and include companies that joined Toray Group in fiscal 2014 or later.
- The calculation method for the baseline year of fiscal 2013 and for fiscal 2023 onward changed to multiplying greenhouse gas emissions by the degree of financial control Toray Industries has over the individual subsidiary, in accordance with the GHG Protocol, the international standard.
- The calculations for fiscal 2020 through fiscal 2022 are based on multiplying greenhouse gas emissions by equity share. Using the same calculation method as in fiscal 2023, which multiplies by the degree of financial control Toray Industries has over the individual subsidiary, greenhouse gas emissions for fiscal 2022 are 5.12 million tons.
Toray Group Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 3) and Calculation Method
In addition to Scope 1 (direct emissions from plants, offices, and vehicles, etc. owned by the Group) and Scope 2 (indirect emissions resulting from the production of electricity and other energy consumed by the Group), Toray Group also calculates Scope 3 emissions (other indirect emissions).
FY 2024 Scope 3 Emissions
(10,000 tons-CO2eq)
| Category 1: Purchased goods and services | 854.7 |
|---|---|
| Category 2: Capital goods | 75.2 |
| Category 3: Fuel and energy related activities | 93.3 |
| Category 4: Upstream transportation and distribution | 17.3 |
| Category 5: Waste generated in operations | 0.8 |
| Category 6: Business travel | 0.6 |
| Category 7: Employee commuting | 2.1 |
| Category 8: Upstream leased assets | 0.5 |
| Category 9: Transportation and delivery (downstream) | 2.8 |
| Category 10: Processing of sold products | ─ |
| Category 11: Use of sold products | 146.7 |
| Category 12: End-of-life treatment of sold products | 441.9 |
| Category 13: Leased assets (downstream) | 1.1 |
| Category 14: Franchises | 0.0 |
| Category 15: Investments | ─ |
| Total | 1,637.1 |
Calculation Method for Scope 3
| Category | Calculation Method |
|---|---|
| 1. Purchased goods and services | Calculated by multiplying the volume of purchased products and services (physical and monetary data) by the emission factor for each item. (Used values from the Inventory Database for Environmental Analysis (IDEA), industry-related database charts, and those provided by suppliers.) |
| 2. Capital goods | Calculated by multiplying the expenditure amount for purchased capital goods (amount of capital investment) by the emission factor used to calculate GHG throughout the supply chain. (See IDEA.) |
| 3. Fuel and energy related activities |
Fuel:
Calculated by multiplying the amount of purchased fuel by the emission factor for the fuel type. (See IDEA.) Electricity: Steam (heat):Calculated by multiplying the input data of electricity procured from power companies by the average emission factor of all power sources, which is based on the emission factor used to calculate GHG throughout the supply chain. (See IDEA.) Calculated by multiplying the input data of procured heat by the emission factor used to calculate GHG throughout the supply chain. (See IDEA.) |
| 4. Upstream transportation and distribution |
Raw Materials: Products:Emissions for transportation are calculated by multiplying weight and distance by emission factors for each type of transportation. (See Shippers’ Guide to Energy Conservation Promotion, 7th Edition, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.) Also, emission impacts from storage and loading/unloading are minimal and therefore not included. Emissions for transportation are calculated by multiplying weight, distance, and loading rate by emission factors for each type of transportation, which is based on the emission factor used to calculate GHG throughout the supply chain. (See IDEA.) Also, emission impacts from loading/unloading are minimal and therefore not included. |
| 5. Waste generated in operations | Calculated by multiplying the amount of waste for each type of waste by the emission factor applicable to type of waste, which is based on the emission factor used to calculate GHG throughout the supply chain. (See IDEA.) |
| 6. Business travel | Calculated by multiplying the total number of employees by the emission factor, which is based on the emission factor used to calculate GHG throughout the supply chain. (See IDEA.) |
| 7. Employee commuting | Calculated by multiplying the total number of employees and the average number of days of operation by the emission factor, which is based on the emission factor used to calculate GHG throughout the supply chain. (See IDEA.) |
| 8. Upstream leased assets | Calculated by multiplying floor area of relevant building by the emission factor per unit of floor area, which is based on the emission factor used to calculate GHG throughout the supply chain. (See IDEA.) |
| 9. Transportation and delivery (downstream) | Calculated by taking the emissions related to upstream transportation and distribution (Category 4) and factoring in the emission shares based on whether Toray or a third party is the shipper. Only emissions related to transportation and distribution up to the first sales destination are included in the calculation. |
| 10. Processing of sold products | Toray Group primarily sells a wide variety of materials and substances as intermediate goods for various applications. It is difficult for the Group to ascertain how its materials and substances are processed into final products, making it impossible to reasonably estimate the corresponding emissions. Accordingly, this category has been excluded from the Group’s emissions calculations. |
| 11. Use of sold products | For products that generate emissions during the direct use stage, emissions are calculated by multiplying the sales volume in the reporting year by the product’s estimated lifetime emissions (estimated using a standard scenario established by Toray Group for each product concerned). The main products that generate emissions during the direct use stage include manufacturing plants, equipment, devices, and machines provided by Toray Engineering Co., Ltd., as well as dialysis-related and blood purification devices from Toray Medical Co., Ltd. |
| 12. End-of-life treatment of sold products | Calculated by multiplying the sales volume of products sold by Toray Group to third parties by the waste emission factors associated with each product (assuming complete combustion and incineration) |
| 13. Leased assets (downstream) | Calculated by multiplying the floor area of relevant buildings by the emission factor per unit of floor area, which is based on the emission factor used to calculate GHG throughout the supply chain. (See IDEA.) |
| 14. Franchises | Considered to be zero, as the Toray Group does not have any franchises |
| 15. Investments | Not calculated, due to low relevance to Toray Group |
Note: The number of companies included in the calculations differs by category.
Related Information
Toray Group has obtained third-party assurance of its Scope 1, 2 and 3 greenhouse gas emissions from LRQA Limited.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 1 and 2) for Toray Industries and Its Group Companies in Japan
In fiscal 2024, greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 and 2) at Toray Industries and its group companies in Japan decreased by 3.5% compared to the previous fiscal year. Greenhouse gas emissions per unit of revenue improved by 10.9% compared to the previous fiscal year, due to efforts to reduce emissions and an increase in sales revenue. This resulted in a 43.0% reduction compared to fiscal 2013.
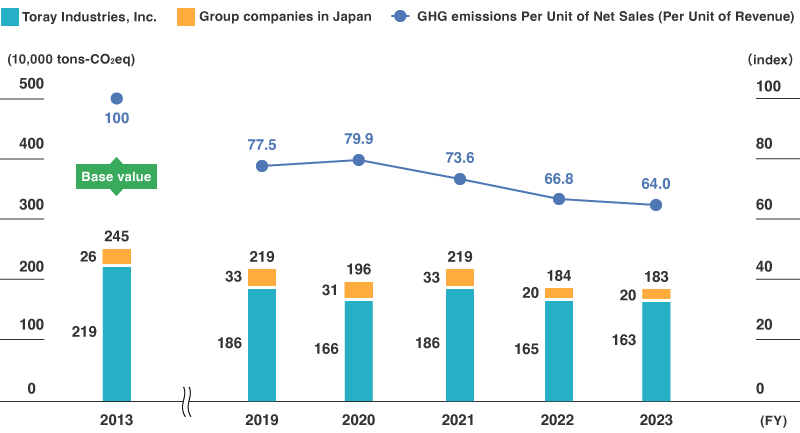
Notes:
- Figures for the baseline year of fiscal 2013 are calculated using Japanese GAAP and include companies that joined Toray Group in fiscal 2014 or later.
- The calculation method for the baseline year of fiscal 2013 and for fiscal 2023 onward changed to multiplying greenhouse gas emissions by the degree of financial control Toray Industries has over the individual subsidiary, in accordance with the GHG Protocol, the international standard.
- The calculations for fiscal 2020 through fiscal 2022 are based on multiplying greenhouse gas emissions by equity share.
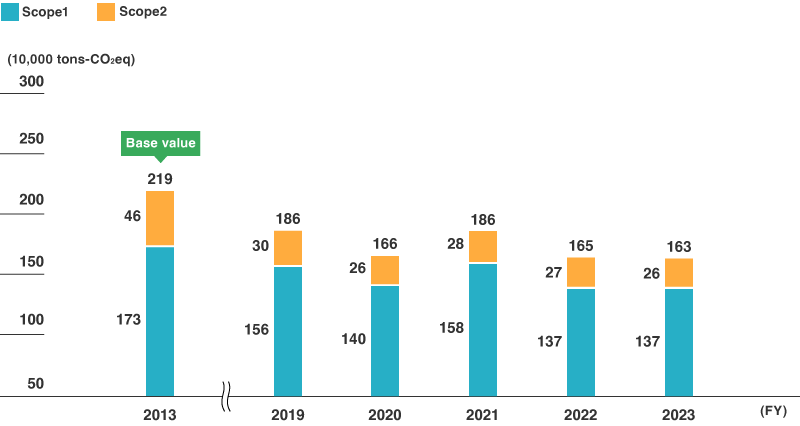
Installing Renewable Energy Systems
Increase in solar power generation capacity (%)
- ■Reporting scope
- Toray Group
- ■Target
- At least 10% higher than fiscal 2022 (Fiscal 2025)
Result in fiscal 2024
182%
 Solar power generation system at Toray Industries Ishikawa Plant
Solar power generation system at Toray Industries Ishikawa PlantUnder its CSR Roadmap 2025, Toray Group has set the rate of increase for solar power generation capacity as a KPI and is focused on the adoption of renewable energy systems.
In fiscal 2024, the expansion of solar power systems at the Toray Industries Shiga Plant, new installation at the Company’s Ishikawa Plant and system expansion at group company plants in China resulted in an 182% increase in capacity. Going forward, the Group will continue to promote the installation of solar power systems.
In addition, the Tokai Plant of Toray Industries began co-combusting sludge fuel, which is carbon neutral, as boiler fuel from fiscal 2017.
- Renewable energy generated in fiscal 2024
- 104,609 MWh
Toray Group has installed solar power generation facilities at the following plants:
| Toray Industries, Inc. |
|
|---|
| Group companies in Japan |
|
|---|
| Group companies outside Japan | |
|---|---|
| America | |
| United States |
|
| Europe | |
| Italy |
|
| Hungary |
|
| Asia | |
| East Asia |
|
| Southeast Asia |
|
Substantial Use of Renewable Electricity at Toray Industries
Toray Industries signed a green power supply service4 agreement with Mitsui Fudosan Co., Ltd. for the Toray head office located in Tokyo's Nihonbashi Mitsui Tower.
By utilizing, through Mitsui Fudosan, the environmental value of the wind power facilities that Electric Power Development Co., Ltd. operates, Toray’s head office has effectively used 100% renewable energy since April 2022. On a global basis, the estimated annual reduction in greenhouse gas emissions should be around 1,500 tons-CO2.
In April 2023, the Nagoya Branch of Toray Industries, which is located in the Nagoya Mitsui New Building, introduced a Green Power Supply Service, allowing it to effectively procure renewable energy. This same step was taken by the Osaka Head Office, which is located in the Nakanoshima Mitsui Building, in April 2024, and by the Chugoku & Shikoku Branch, which is located in the Hiroshima Train Vert Building, in April 2025.
In addition, at the Shiga Plant and the Gifu Plant of Toray Industries, a portion of the electricity used in the production process for Ultrasuede was switched to CO2-free power sources starting in April 2024 in order to reduce CO2 emissions from electricity consumption. This is expected to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 7,100 tons-CO2 annually.
- 4 Green power supply service: A unique service developed by Mitsui Fudosan that uses non-fossil fuel energy certificates to provide electricity to the tenants of its office buildings, which is effectively generated using 100% renewable energy.
Initiatives to Protect the Ozone Layer
Toray Industries ceased using chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) in all manufacturing processes and stopped purchasing CFCs for use in refrigeration equipment in 1994. The Company finished upgrading refrigeration equipment using CFCs in fiscal 2019.
Related Information
See the following webpage for information on climate-related disclosures in line with the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
Click here for the main initiatives for CSR Guideline 3, "Safety, Accident Prevention, and Environmental Preservation" in CSR Roadmap 2025.